Porsche Taycan Thermal Management
Thermal Management 🌡 is a major challenge of Electric Vehicles 🚗🔌
Contrary to IC Engine, the game for EV is to allocate existing Heat Flows ♨️ in the 🚘 and store them in available thermal masses
For example, on the Porsche Taycan, multiple components need Temperature control 🌡:
➡️ Drive unit: PSM eMotor, gearbox, inverter
➡️ Battery system🔋
➡️ On-Board Charger (OBC) 🔌
➡️ HV-Booster (to transform 400V into 800V)
➡️ DC-DC ⚡️converter (to transform 800V Battery voltage into 400V, 48V, 12V)
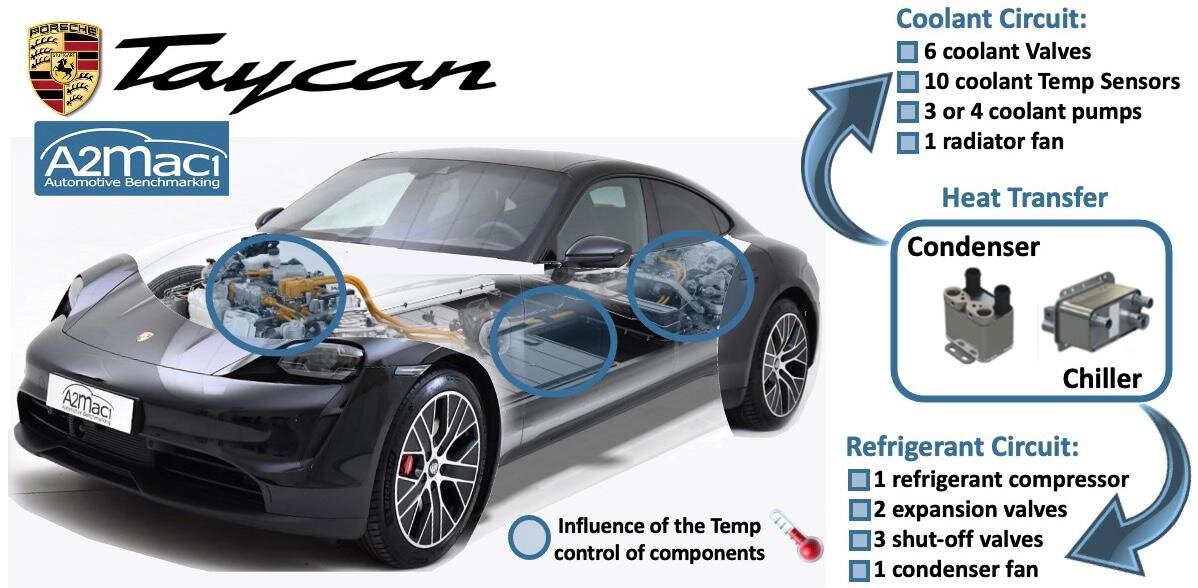
In total, the Porsche Taycan uses more than 100 Hydraulic Interconnectors for Temp control 🌡
3 different temperature levels can be distinguished in the coolant circuit of the Taycan:
1️⃣ Heating circuit with up to 90°C coolant 🥵Temp
2️⃣ Medium Temp circuit [40-65 °C]
3️⃣ Low Temp < 40 °C 🥶
These circuits can be connected or separated 🔀 via valves, allowing to independently control all components
The global thermal management 🌡 is based on a refrigerant and a coolant circuit using a chiller (in the low-temperature circuit ❄️) and an indirect condenser (in the heating circuit ☀️ for condensation)
The thermal management control unit regulates the circuits within a millisecond based on Temp sensors 🌡 and consumed power ⚡️
More details? ➡️ A2Mac1 - Automotive Benchmarking